Cardiovascular Health: A Comprehensive Approach
Maintaining optimal cardiovascular health requires a multifaceted strategy that addresses various aspects of an individual’s lifestyle and medical needs. This comprehensive approach aims to prevent and manage cardiovascular conditions for long-term heart health.
Anatomy and Function of the Heart
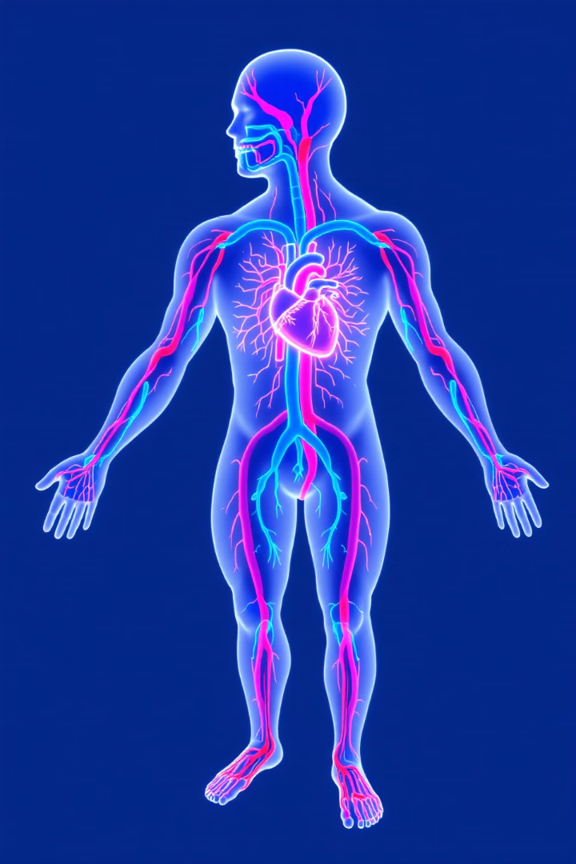
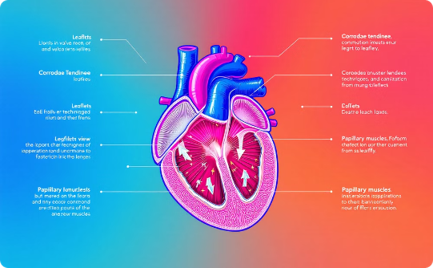
The human heart is a remarkable muscular organ that serves as the central pump of the cardiovascular system. It is divided into four distinct chambers, each playing a crucial role in the efficient circulation of blood throughout the body.
The heart’s intricate structure includes valves, arteries, and veins that work in harmony to ensure the continuous flow of oxygenated blood to vital organs and tissues. Understanding the anatomy and physiology of this vital organ is essential for maintaining overall cardiovascular health.
Understanding Blood Circulation
Common Cardiovascular Conditions
Hypertension: Causes and Management
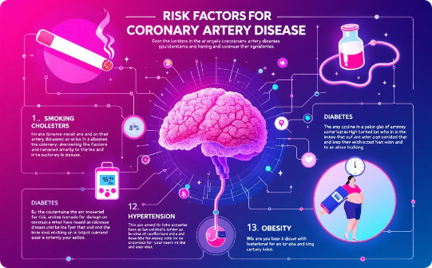
Coronary Artery Disease: Risk Factors and Prevention
Heart Attacks: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
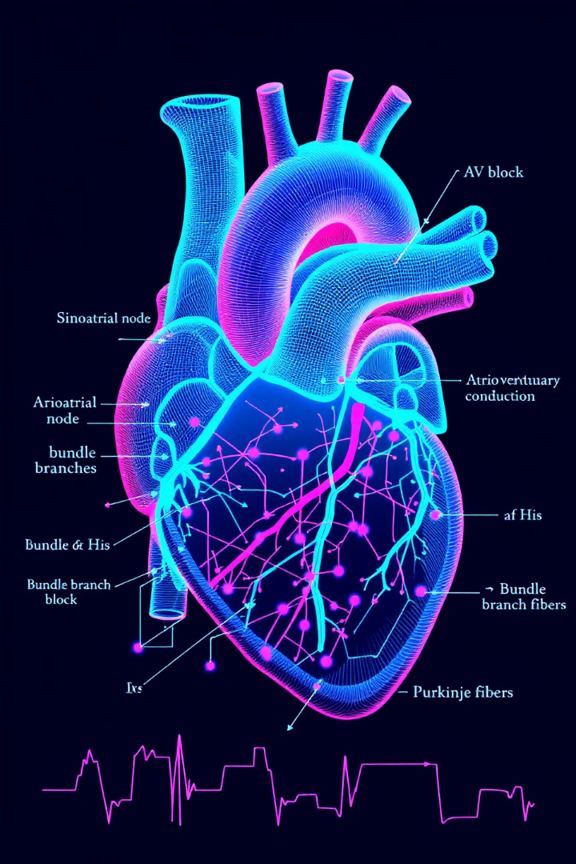
Arrhythmias: Types and Treatments
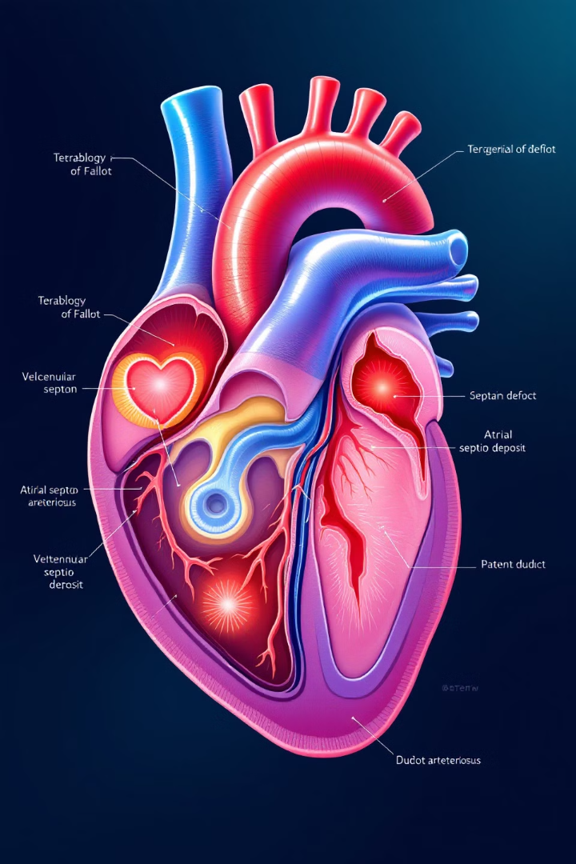
Congenital Heart Defects: Causes and Treatments
Advances in Cardiac Imaging and Diagnostics
Cutting-edge cardiac imaging technologies have revolutionized the field of cardiology, enabling earlier detection, more precise diagnoses, and personalized treatment plans. From high-resolution CT scans to state-of-the-art MRI and PET imaging, clinicians now have unprecedented visibility into the heart’s structure and function.
Innovations in echocardiography, including 3D and transesophageal imaging, provide real-time, dynamic assessments of cardiac performance. Meanwhile, advancements in cardiac biomarker testing allow for more accurate identification of cardiac injury and risk stratification.
Innovations in Cardiac Interventions and Surgeries
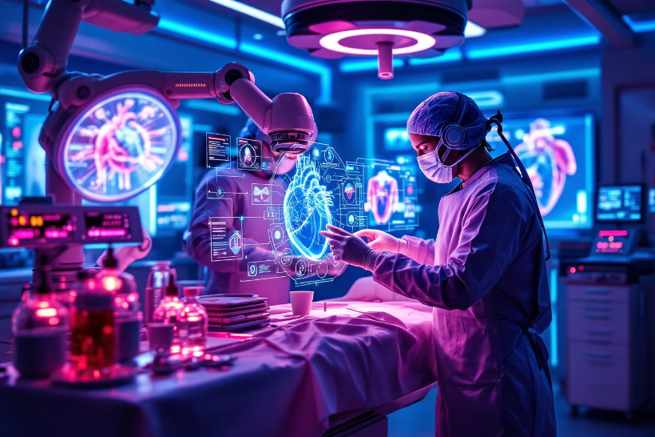

Groundbreaking advancements in cardiac interventions and surgeries are revolutionizing cardiovascular care. Minimally invasive procedures, such as transcatheter valve replacements and robotic-assisted coronary bypasses, offer less invasive alternatives to traditional open-heart surgeries.
Emerging technologies, like 3D printing and virtual reality, are enhancing surgical planning and precision, leading to improved patient outcomes and reduced recovery times.